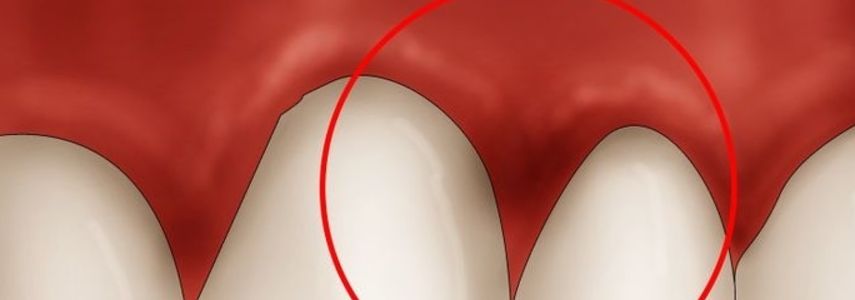
Black gums may not cause you any kind of pain, but they certainly have a strong impact on aesthetics and smile.
The gums, in a healthy condition, should have a pink color. The alteration of their color is therefore an alarm bell with respect to the possible presence of specific pathologies.
What are the causes of black gums?
Black or too dark red gums can derive from multiple causes, not always pathological. The most common are the following:
- hereditary factors
 o pigmentation of an ethnic specificity
o pigmentation of an ethnic specificity - smoking abuse
- periodontitis
- poor oral hygiene
- particular drug therapies
- excess melanin
- drug use
- presence of amalgam on the gingival tissue
Let’s go into the specifics of the different causes.
1. Hereditary or species factors
Among the non-pathological causes we have both hereditary factors and characteristic factors of the species. People with dark skin have an excess of melanin, also present in the gums, this leads to a variation in the pigmentation that makes them appear darker.
2. Smoking
Smoking is also not a direct pathological cause, but the excessive use of cigarettes has serious consequences for the health of the teeth. Smoking increases the chances of getting gum infections that can gradually degenerate into periodontitis.
3. Periodontitis
Black gums are in fact a symptom frequently related to periodontal disease. In particular, in an advanced stage of the pathology necrosis (i.e. death) of the gingival tissues can occur, which in fact become black.
4. Poor oral hygiene
Black gums are also a direct consequence of poor or neglected oral hygiene. The accumulation of plaque and tartar near the gingival sulcus irritates the gums with ease. If the tartar is not removed with a deep dental cleaning, the inflammation spreads to the whole gingival tissue causing a gradual redness. Not intervening promptly could complicate the situation up to a periodontitis.
5. Special drug therapies
Some drugs, including antimalarial drugs, some types of antidepressant drugs can cause a gradual blackening and swelling of the gums, especially if the treatment is protracted over time.
6. Excess melanin
There are some rather rare diseases that cause an excess of melanin and therefore the problem of black gums. These include: Addison’s disease affecting the endocrine glands; Von Recklinghausen’s disease affecting the bones; Peutz-Jeghers syndrome which affects the intestine.
7. Use of drugs
There are drugs, in particular cocaine, which, if taken by rubbing on the oral mucous membranes, cause the problem of black gums over time.
8. Presence of amalgam in the gingival tissue
Following a dental therapy, such as the devitalization of a tooth, it is possible that some amalgam particles may detach and stain the gums with black. In this case the gums will return to their natural color simply by undergoing a professional oral hygiene session.
Black gums in pregnancy
In pregnancy, the gums may appear black because it increases the predisposition to the accumulation of bacteria and plaque, with consequent redness and inflammation of the gums. You can prevent the phenomenon of black gums in pregnancy by planning a session of deep oral hygiene and carefully taking care of daily oral hygiene.
Black gums during teething
Black gums in babies are the first sign of the teething phase. In fact, the teeth that emerge are anticipated by a progressive redness and swelling of the gums. The phenomenon of black gums among infants is therefore very common and should not cause any concern. At the end of the teething phase, the gingival tissue will return to its normal pink color.
As it is easy to deduce, black gums have multiple causes. By identifying a color change even with the naked eye, it is therefore always advisable to consult your dentist for an appropriate diagnosis.