The bleeding gums are a frequent phenomenon, often overlooked because it is painless and it tends to be stored with a common thought: “it will pass by itself”.
Bleeding gums: what’s behind it?
On May 12th, European Healthy Gum Day was celebrated, on this occasion quite alarming data were released: in Europe there are 8 out of 10 people, over the age of 35, who have a gum disease. In a global perspective, on the other hand, there are about 743 million people who have been diagnosed with severe periodontitis and who risk losing their teeth.
The first alarm bell with respect to one of the pathologies affecting the gums is precisely bleeding.
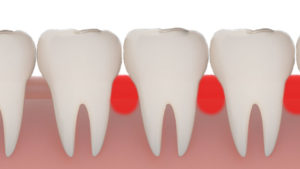
In fact, bleeding gums are not always a problem related to tooth sensitivity or other temporary situations, such as irritation or microlesions. There are also much more serious pathologies that include the reddening and bleeding of the gums, including some forms of leukemia or a dysfunction of the body in the coagulation of the blood.
Bleeding gums: pregnancy and hormonal changes
Bleeding gums could also be a frequent condition for women, especially during periods of hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy. In fact, during the gestation phase the gums are more sensitive to bacterial attacks and it is therefore likely that the gums may bleed.
Except for these cases listed above, most often the gums bleed because at the base there is neglected oral hygiene.
Bleeding gums: cases of gingivitis
The bleeding of the gums is one of the first symptoms of gingivitis, that is an inflammation of the gums due to the presence, on the gum line, of an accumulation of tartar.

The bacterial plaque, in the cases in which it is not correctly removed, sediments until it becomes tartar. The presence of tartar triggers gum infection and its relative bleeding.
Gingivitis is the first stage of a more complex pathology: periodontitis. Neglecting the problem therefore means facing a possible loss of teeth. In case of periodontitis, bleeding of the gums leads to an irreversible consequence.
The importance of timely intervention
All the pathologies described above are reversible if the first symptoms of gum bleeding occur.
When the gums bleed it is important to stop the progression of the infection. A check-up by the dentist can bring the alarm back thanks to an early diagnosis and adequate therapy.
Often, for many cases, everything can be solved with a single session of deep oral hygiene. In more serious cases, with advanced gingivitis specific dental therapy is required.
The magazine cleaning of the gum pockets and proper oral hygiene at home can certainly be a valid remedy for bleeding gums.
To these virtuous behaviors, however, others must be added concerning the lifestyle:
- reduce consumption of smoke and alcohol, for example, substances that promote irritation, weakening and bleeding gums;
- have a balanced diet and reduce the risk of obesity.
Preventing gum bleeding is the first step in preserving your natural teeth; don’t neglect the bleeding gums, or the signals that our body transmits to us, can avoid far worse problems.