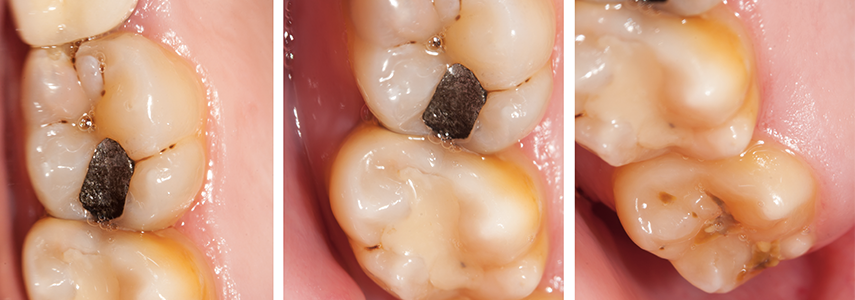
On February 23, 2021, the National Plan for the elimination of dental amalgam was published on the website of the Ministry of Health.
A government action that is part of the European framework, following the Minamata Convention on mercury, which provides for the adoption of measures to progressively eliminate dental amalgam throughout Europe.
Why is dental amalgam harmful?
Dental amalgam, used in the past for the devitalization of teeth following a root canal treatment, contains mercury, a potentially toxic metal.
The mercury contained in fillings can slowly crumble due to malocclusion, bruxism or the heat of food, to the point of causing health consequences in fragile or particularly predisposed subjects.
Mild mercury poisoning can cause:
- chronic fatigue;
- migraine;
- decreased appetite;
- continuous thirst;
- anemia;
- sleep disorders.
What the European Regulation provides
The goal for the elimination of dental amalgam had already been implemented by all the states of the European Union in 2017, with the drafting of a European Regulation.
Even Italy, since 2017, has committed itself to this by placing limits on the production, use and removal of amalgam.
The European plan prepares what should be the necessary actions that would lead to the progressive discontinuation of the use of dental amalgam in dentistry, with the ultimate aim of achieving a complete elimination of this use by 31 December 2024.
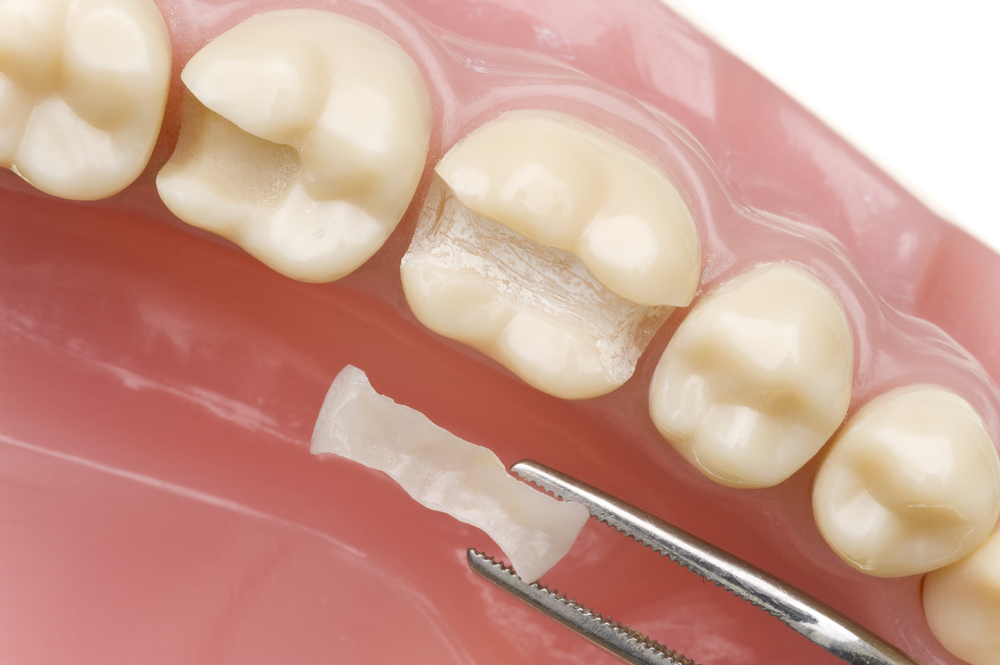
Remove amalgam from devitalized teeth in the past
The National Plan aims to activate awareness-raising paths towards patients, informing them about all the problems related to the use of dental amalgam and making them aware of the importance of the use of alternative materials for the devitalization of the teeth.
Dentists will also play a fundamental role in this.
The dentist will have the task of informing the patient and proposing alternative materials, biocompatible and harmless to health.
The patient can always decide to remove old amalgam fillings and replace them with ceramic and biocompatible composite fillings, it is important, however, that there is always an evaluation of the clinical case by the dentist and that the removal of the filling takes place in a structure that guarantees maximum safety for the patient.