If a tooth breaks, splinters or for other types of pathologies it erodes or wears out, it is likely that dental reconstruction should be used.
The missing parts of the tooth are recomposed thanks to the use of particular materials with the possibility of restoring both aesthetic and chewing functions.
Until recently, the materials used for dental reconstruction were mainly made of metals. In particular, the use of amalgam was widespread, a compound of metals, including silver, malleable, thanks to the presence of mercury and the gray color, which was used to restore the cavities left by the export of caries (the so-called fillings dental). Those who have never undergone new tooth restorations recently may still have such reconstructions in their mouths.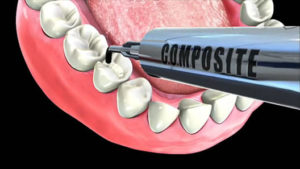
The use of silver amalgam has been completely abandoned over the years because the mercury component has proven to be particularly harmful to the nervous system and kidney system.
Today the trend is to use materials that do not contain metals, in particular the choice recommended by the dentist is between ceramic and composite.
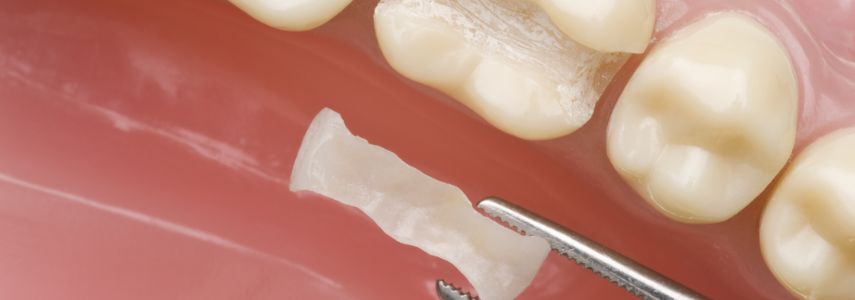
Ceramic
It is a very resistant material that is fixed to the tooth with the aid of a cementing substance, the ceramic cannot be modeled directly by the dentist, therefore, before being positioned, it must be worked in a specialized laboratory. Starting from our dental impressions and intervention needs, the dentist will be able to use ceramic for partial tooth reconstructions or to create prostheses that will completely replace a fallen tooth.
Advantages of ceramics
- Abrasion resistance
- the therapy has a long duration over time
- excellent aesthetic result
A fundamental part is the design phase, it is important that a skilled professional realizes the ceramic parts with a particular attention to thickness and resistance so as not to general any malocclusion problems.
Composites
The choice of composites is very common in dental reconstruction and is also the cheapest. Composites are mainly made of resin, a malleable substance that the dentist himself can work on and adapt to the need for therapy. Once the composite is positioned in the tooth cavities, the material is fixed thanks to exposure to a light source, a chemical reaction in fact causes the substance to harden to make it fixed and stable.
Advantages of composites:
- adapts to the tooth ensuring continuity between the tooth and the reconstructed part
- no need for retouching
- reproduces the natural color of the tooth
The disadvantage of composites is the tendency to abrasion over time and, compared to ceramic, guarantees a lower surface gloss.
In any case, the choice between ceramic or composite must be examined by the dentist who has the specific task of evaluating the most appropriate solution on a case-by-case basis. In fact, it is not only a matter of preference of one material over another, but in the overall treatment of one dental reconstruction or implant of prosthesis, the evaluation is carried out on the basis of the patient’s needs, aesthetic and functional functions (of chewing for example) with personalized care that can always guarantee the best result for each individual.