A diagnosis of pericoronitis characterizes inflammation of the gum due to the eruption of a tooth. It is an acute inflammation very often linked to the eruption of wisdom teeth or third molars.
Pericoronitis and impacted or partially impacted teeth
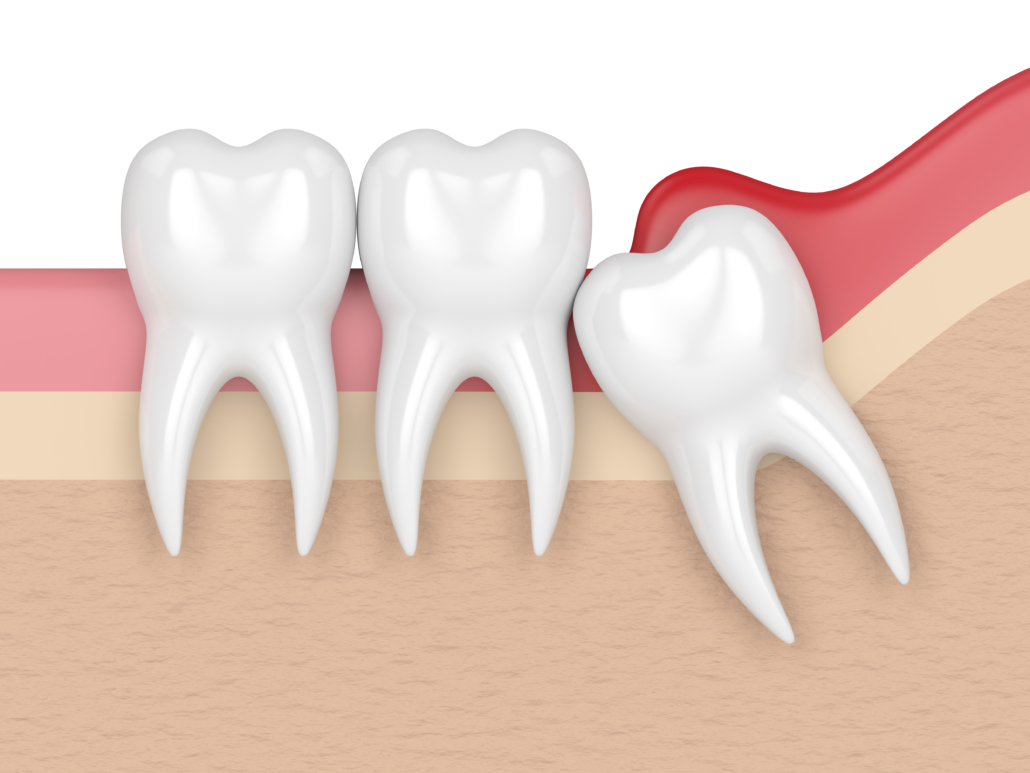
The problem of impacted or partially impacted teeth particularly concerns wisdom teeth or third molars. This drawback is due to a purely evolutionary question.
The function of the third molars is in fact linked to the habits of our ancestors. The function of the third molars is in fact linked to the habits of our ancestors.
Evolution has led man to new eating and living habits and, while the temporomandibular system has adapted by causing the mandible to shrink, the number of teeth in the arch has remained unchanged. For this reason, wisdom teeth, which to date do not have a specific function for the purpose of chewing or phonation, do not find the right place in the arch and are often included or partially included.
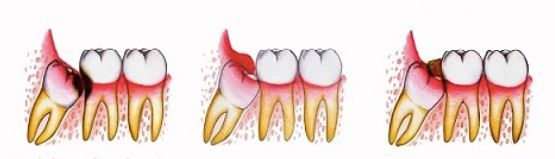
Inflammation of the gum due to an impacted tooth is diagnosed as pericoronitis.
How does gum inflammation develop?
A tooth is defined as included when its root is included in the bone, while the crown is contained in a sac of fluid called the pericoronary sac.
If the tooth fails to erupt properly and remains included or partially included, the pericoronary sac breaks and the crown, which is no longer protected by the liquid, becomes a pocket in which food residues can accumulate and facilitate the proliferation of bacteria. .
In these particular conditions, inflammation of the gum or pericoronitis originates.
Pain and discomfort of inflammation of the gum
Symptoms of pericoronitis are:

- swollen gum;
- pain when brushing your teeth;
- presence of pus;
- persistent bad breath;
- pain that extends to the neck and ear;
- difficulty chewing and swallowing;
- headache.
In the presence of these symptoms, the timeliness of an intervention by the dentist is essential.
In fact, pericoronitis could worsen and inflammation of the gum cause other complications including high fever and swelling spread up to the cheek.
What type of surgery for pericoronitis
To ascertain the diagnosis of pericoronitis, the dentist will carry out a first check-up visit including diagnostic imaging.
Imaging can rule out other pathologies with similar symptoms such as periodontitis or pulpitis.
The dentist will check the progress of the inflammation of the gingiva and will choose the most suitable therapy for the patient’s situation.
In cases of advanced pericoronitis, the dentist may decide to intervene surgically to remove the infected part of the gum or, following a therapy to quell the inflammation, proceed with the extraction of the included or partially included tooth.
Extraction is always the last of the possibilities that the dentist takes into consideration, in fact the goal is always to preserve natural teeth, even when it comes to wisdom teeth.