We focus on oral leukoplakia because it is a potentially dangerous pathology, unlike other lesions of the oral mucosa in fact, it can degenerate into a cancerous lesion.
How does leukoplakia manifest?
The leukoplakia looks like one white spot in the oral cavity, the diagnosis of this pathology is made by exclusion, because the white spot in question, in the case of leukoplakia, cannot be associated with other clinical or histopathological conditions that present the same symptom, ie a white spot, such as also referred from theWorld Health Organization.
The causes of the origin of leukoplakia in the oral cavity are not yet clear, but from an accurate analysis of clinical cases over time, an important correlation emerged between smokers and the onset of the disease.
What variables affect the onset of leukoplakia?
The damage of smoke to the teeth and more generally to the oral cavity, are quite known. Indeed, one of the main consequences is soft tissue irritation. The continuous irritation of the oral mucosa leads to its lesion and in the specific case of leukoplakia, this can degenerate into a malignant neoplastic lesion, ie a tumor.
All those clinical conditions or those linked to incorrect lifestyles become worrying, which can cause lesions of the oral cavity:
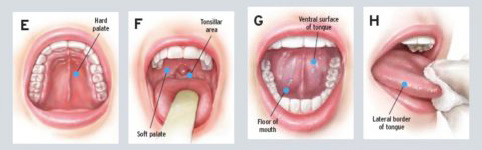
From the observation of clinical cases it has also emerged that the lesions become more easily cancerous if they appear on the oral floor or on the tongue.
Characteristics of the oral lesion
The presence of a white plaque is the main symptom, white is given by an increase in keratin on the affected part.
The mere presence of white plaque is a symptom of a homogeneous flat leukoplakia.
The presence of a white plate with a verrucous aspect, the verrucous leukoplakia, can also be manifested.
If then the plaque in addition to having an irregular, verrucous surface, it also has white and other reddish parts, we are in the presence of an inhomogeneous fissured leukoplakia.
How is leukoplakia treated?
The small lesions of the oral cavity can disappear with the elimination of the causes that triggered its origin. Abolishing smoking and alcohol, for example, allows an immediate regression of the pathology.
In more serious cases, on the other hand, surgical intervention and subsequent biopsy of the excised tissue is necessary to verify the nature of the lesion and exclude any suspicion.
The oral lesions must never be underestimated. Especially in the case of this specific disease of the mouth, identifying and intervening in time on the pathology allows the patient to avoid all the painful and dangerous complications of oral cancer.
Only a dentist with proven experience is able to diagnose such complex pathologies, prevention, through periodic follow-up visits, can save lives in these cases.