The lack of balance between oxidizing substances and antioxidant substances determines an abnormal health condition called oxidative stress.
It is a physical ailment that presents a set of symptoms:
- tiredness;
- fatigue;
- skin aging;
- inflammation of the oral cavity.
Oxidative stress: the role of free radicals
Free radicals are oxidizing chemical compounds that the human body produces through the activities of the metabolism, but these are chemical elements that can damage the body.
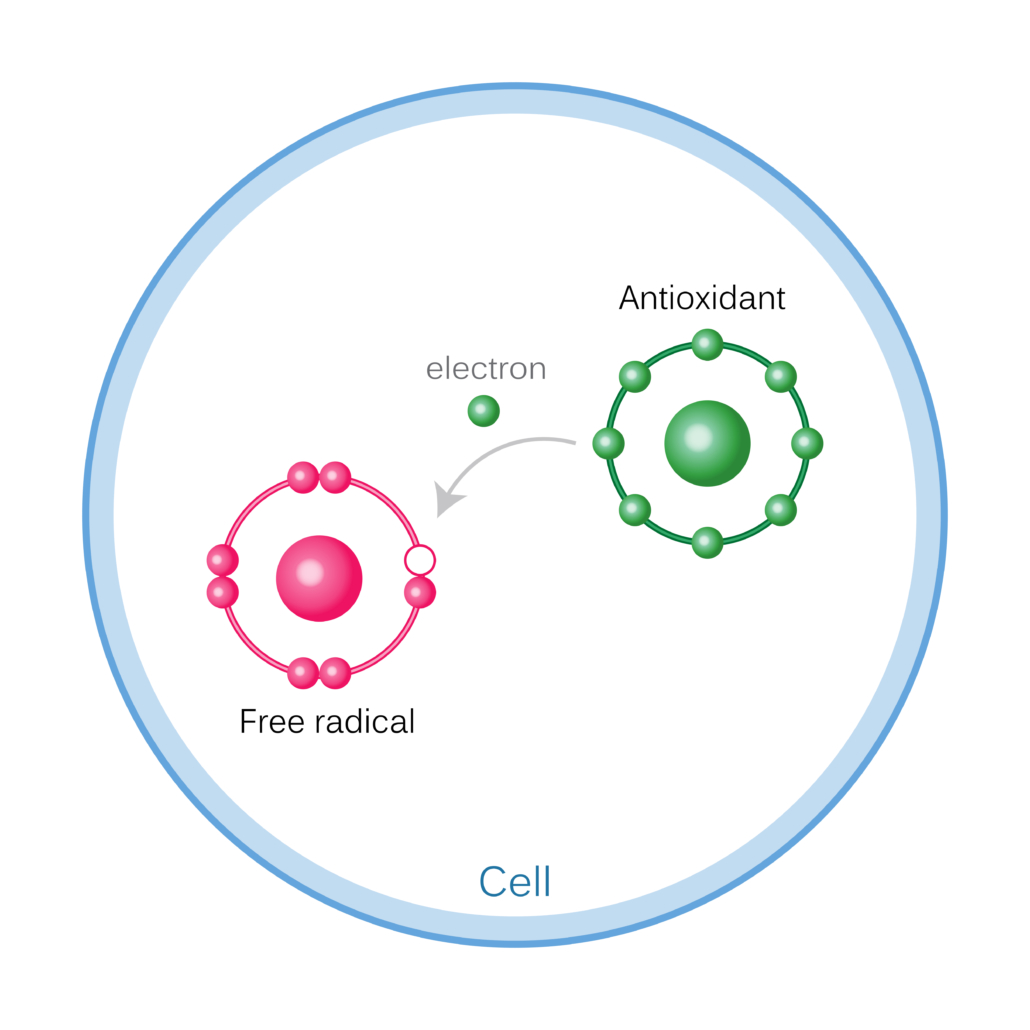
The mechanism by which free radicals attack parts of the organism is very simple: the molecule of a free radical is characterized by one or more unpaired electrons, so it is particularly unstable molecules that tend to capture electrons from other molecules thus making them oxidized molecules and giving rise to a chain reaction, continuing to produce oxidizing substances.
In particular, free radicals ROS – Reactive Oxygen Species are particularly reactive to oxygen and can attack cells such as DNA, proteins or lipids.
When the number of free radicals exceeds that of antioxidant substances, the condition of oxidative stress occurs.
How is the diagnosis made?
Symptoms of oxidative stress are often generic and it is difficult to have an immediate diagnosis. Among the main symptoms are:

- appearance of wrinkles and a progressive aging of the skin;
- feeling of fatigue;
- headache;
- difficulty concentrating;
- gastric disturbances;
- cardiovascular alterations.
Only specific blood tests allow to identify the excessive presence of free radicals or the low presence of antioxidants.
What Causes Oxidative Stress?
The increase in free radicals can be due to a set of variables:
- abitudini alimentari errate;
- diabetes;
- excess alcohol;
- smoke.
How are free radicals reduced?
Antioxidants naturally present in the body are not always able to fight free radicals.

You can get antioxidants through food and in particular by eating foods rich in:
- vitamins A, B, C, E;
- polyphenols contained in fruit;
- foods high in magnesium.
A healthy and correct diet helps the body to fight oxidative stress, but it is possible to increase the intake of antioxidants with food supplements.
Oxidative stress and periodontitis
Periodontal disease is due to an accumulation of bacteria, the excess of free radicals seems to favor the increase of bacteria inside the oral cavity.
Not only that, some studies have also shown that the tissues of the oral cavity are particularly sensitive to damage caused by free radicals, because they allow rapid absorption.

Conversely, the presence of an infection in the oral cavity, such as gingivitis, can lead the body to excess production of free radicals.
The link between oxidative stress and infections of the oral cavity is therefore established, for this reason it is important to balance the presence of oxidants and antioxidants within the body.
In addition to healthy eating and taking supplements, medicine is also focusing on antioxidants to be applied topically. However, contacting your doctor is the first step to take.















