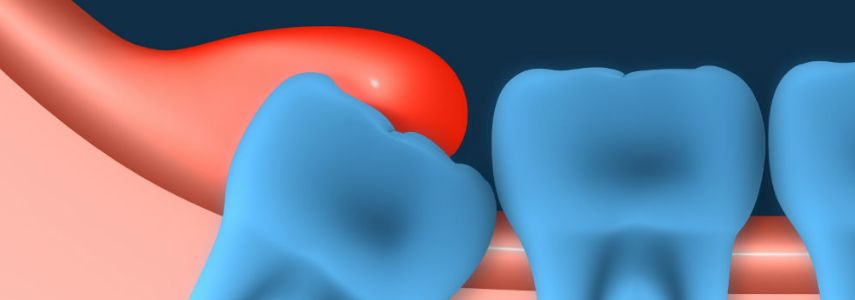
Pericoronitis can be generically defined as the acute inflammation of the gum that surrounds a tooth. In particular, pericoronitis mainly affects the third series of molars, i.e. the so-called wisdom teeth, in the phase of their eruption.
Pericoronitis is the inflammation of the gums caused by the pressure of the tooth during the eruption. 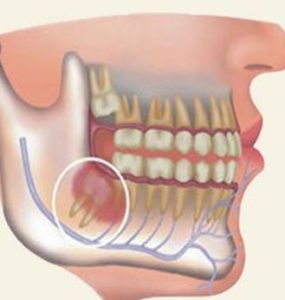
This condition can also occur when the distance between the tooth germ and the rash area is too wide.
Pericoronitis can have several stages, in cases of acute pericoronitis we can also distinguish two different forms of the pathology: a congestive, which precedes and ends with the eruption of the tooth, and a suppurative phase which is an even more serious stage in which inflammation is also involved ear, tongue jaw and throat.
A suppurative pericoronitis can lead to hospitalization and surgery.
Symptoms of pericoronitis
The main symptoms of an ongoing pericoronitis are: soreness, redness, pain and swelling of the gum. The pain often extends to the whole angular area of the jaw and becomes particularly intense during chewing.
In the presence of acute pericoronitis, the pain can also affect the ear and neck with an enlarged lymph nodes. In summary, the alarm bells that can lead you to think about the presence of a pericoronite are the following:
- unusual redness and swelling of the gum
- presence of pus
- swelling of the neck
- fever
- chewing difficulties
- widespread pain even near the ear
- constant headache
If you find one or more of these symptoms listed above, it is appropriate to contact us.
Special contraindications for pericoronitis in pregnancy
More attention is required of pregnant women. If neglected, pericoronitis can have serious consequences for the fetus. A pregnant woman who has been diagnosed with pericoronitis will have to make use of multidisciplinary skills for her treatment: general practitioner, gynecologist, dentist.
Treatment of pericoronitis
If pericoronitis is mild and the pain is limited and not widespread, it is possible to stem the discomfort with rinses of warm salt water. It is also advisable to take special care of daily oral hygiene, using a soft bristle brush.
In cases of acute pericoronitis, the dentist will carefully evaluate the clinical case by opting for two different solutions based on the stage in which the pathology is present:
- The prescription of antibiotics and painkillers in the event that pericoronitis is transient and linked to the next tooth eruption;
- oral surgery in the event that the stage of pericoronitis is particularly advanced, with the aim of eliminating the gingival flap or to definitively extract the wisdom tooth.
To make sure of the diagnosis, even in cases of mild discomfort or superficial redness and swelling of the gum, it is always good to consult your dentist. It is the only way to have specific indications on the best possible therapy for a speedy recovery.