Measuring the pH of saliva can be a particularly useful measure to monitor and prevent any pathologies of the oral cavity.
PH measurement: what is it for?
The dentist is the professional figure responsible for measuring the pH of saliva; a precaution that can be used both for constant monitoring of the state of health of the mouth, and to confirm any preventive therapies for caries or infections of the oral cavity.
What value should the pH of the saliva have?
PH measurement can detect three types:
- acid
- neutral
- alkaline or basic
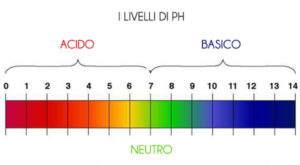 An acidic pH is below a level of 6.5; a neutral pH is in the range between 6.5 and 7.5, a basic or alkaline pH is greater than 7.5.
An acidic pH is below a level of 6.5; a neutral pH is in the range between 6.5 and 7.5, a basic or alkaline pH is greater than 7.5.
The normal condition foresees a neutral pH condition with an interval between 6.5 and 7.5. So both an acidic and a basic pH represent a condition to be monitored.
PH measurement: consequences on teeth when it is acidic
There are foods that more than others contribute to increase the acidic level of salivary pH. Excessive consumption of sweets, carbonated drinks, spirits reduces the salivary pH level, an acidic pH favors the proliferation of bacteria, especially of the cariogenic ones, which begin to attack the tooth enamel.
This occurs when the pH measurement detects a level of 5.5 or less. In mild acid pH situations it is possible to bring it back to normal with the use of fluoride products for oral hygiene. In more critical cases, the dentist may prescribe specific therapies.
PH measurement: the consequences of a basic pH
When the pH level exceeds 7.5, saliva is rich in calcium. Excess calcium settles on the teeth and becomes an ideal base for the accumulation of tartar. The accumulation of layers of tartar becomes a danger for the gums, in fact it is very likely that a gingivitis may develop or worse a periodontitis. In this case, one of the immediate therapies is a professional deep cleansing session.
How to maintain a neutral pH?
In an optimal health condition, saliva always has a neutral pH, but daily it undergoes temporary variations, especially after meals.
In fact, when we ingest food, depending on the nutrients that compose it, the salivary pH can go down or up with respect to the neutral value range. Furthermore, after eating, salivation tends to decrease and saliva cannot counteract the increase in the bacterial load.
To counteract the change in salivary pH level and the reduction of saliva it is essential to brush your teeth thoroughly after each meal.
If you are unable to brush your teeth immediately after meals, a good substitute, useful for restoring pH neutrality, is chewing gum, obviously without sugar. Chewing gum increases salivary intake and restores pH levels to normal. However, this is a sporadic solution and certainly cannot replace the benefits of tooth brushing.
To this it is appropriate to associate a healthy lifestyle, because, for example, smoking is also one of the causes of the drastic drop in salivary pH. Not only therefore a constant and correct oral hygiene, but also a healthy diet and periodic check-ups by the dentist.