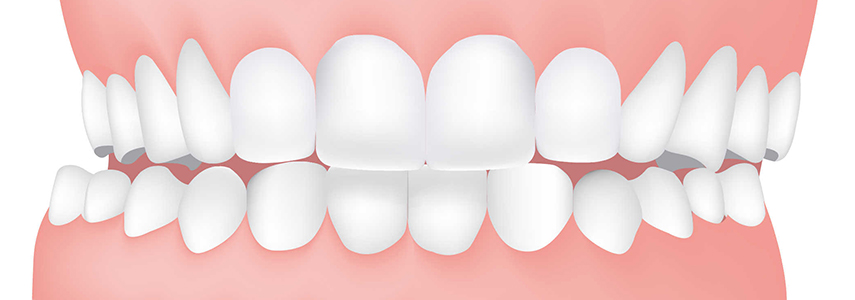
The reverse bite can be a disease that mainly affects children. Reverse bite or cross bite is defined as the situation in which the teeth of the lower arch protrude, even a few millimeters, with respect to the teeth of the upper arch.
The reverse bite and masticatory dysfunction
 The reverse bite can affect the entire arch or a part of it or even a single tooth, it can also affect the front, the back or it can be bilateral or affect only one side. The reverse bite affects not only the teeth, but also the bone in which they are inserted.
The reverse bite can affect the entire arch or a part of it or even a single tooth, it can also affect the front, the back or it can be bilateral or affect only one side. The reverse bite affects not only the teeth, but also the bone in which they are inserted.
In the presence of a reverse bite, what is created is a condition of dental and skeletal asymmetry, which leads to chewing dysfunction, that is, incorrect and asymmetrical chewing.
The pathology of the reverse bite does not present particular symptoms at the beginning, but a lack of diagnosis and treatment could also have quite serious consequences for the health not only of the teeth.
Causes of the reverse bite
There is no single cause in the onset of the cross bite, however there are, in addition to a natural predisposition, a set of variables that can contribute to the appearance of the pathology.
The causes of the reverse bite include:
- swallowing problems;
- breathing problems;
- incorrect posture of the tongue;
- prolonged use of the pacifier or bottle;
- sucking fingers.
During the diagnosis, the dentist will be able to examine in detail the specific causes of the cross bite and proceed with a specific treatment plan.
How to cure the reverse bite
The surgery to correct the crossbite must be as timely as possible because, especially in cases where the patient is a child, the pathology can have consequences for development and growth.
 In fact, a masticatory dysfunction, such as that incurred in the presence of a cross bite, leads the temporomandibular joints to work in an asymmetrical way with consequences on the entire body posture. Incorrect chewing also has effects on digestion and the correct assimilation of food.
In fact, a masticatory dysfunction, such as that incurred in the presence of a cross bite, leads the temporomandibular joints to work in an asymmetrical way with consequences on the entire body posture. Incorrect chewing also has effects on digestion and the correct assimilation of food.
Dental therapy for reverse bite treatment depends on the specific clinical case, in most cases it is corrected through orthodontic therapy.
The use of an orthodontic appliance for the correction of the cross bite is always recommended for patients of developing age. In fact, at this stage the bone structure is not yet definitive and therefore orthodontic movements are facilitated making the therapy effective and permanent over time.
In cases where the cross bite is the consequence of an incorrect tongue posture, dental rehabilitation therapies are also accompanied by muscle rehabilitation therapies to prevent the problem from recurring. In adult patients, orthodontics may not be sufficient or in any case could lead to partial results, in these cases it is likely that oral surgery should be carried out.
If you need advice on a reverse bite problem, you can contact us to schedule a first visit.