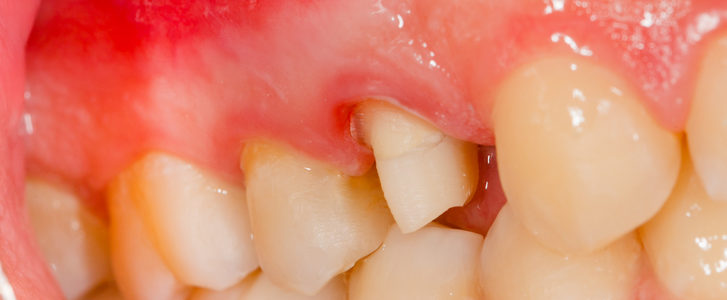
Having swollen gums is a very common and widespread condition. Many patients underestimate the problem because it is equally common to think that it is a disorder that sooner or later will go away on its own. In fact, swelling in the gums can be a wake-up call for various pathologies, let’s find out which ones together.
Swollen gums: what can be the causes
At the basis of the swelling of the gums there can be several reasons, some more trivial and others decidedly more complex.
1. Poor oral hygiene
One of the most common causes and on which it is also easier to intervene is poor or incorrect oral hygiene.  The proliferation of bacteria inside the oral cavity favors the accumulation of plaque which is deposited not only on the surface of the teeth but also on the gums. The situation is worsened by the stratification of the plaque and the appearance of tartar.
The proliferation of bacteria inside the oral cavity favors the accumulation of plaque which is deposited not only on the surface of the teeth but also on the gums. The situation is worsened by the stratification of the plaque and the appearance of tartar.
In these specific conditions it will be quite easy to notice a slight swelling of the gums and their redness. The swollen and red gums will also tend to bleed when any pressure is exerted, for example when brushing the teeth.
Neglecting this type of condition could lead, in a very short time, to the onset of a pathology that can cause multiple damage to our health: gingivitis, or inflammation of the gums.
How to intervene on the swelling of the gums caused by poor oral hygiene?
The answer is simple, planning with your dentist a couple of deep cleaning sessions per year, which obviously must be accompanied by regular domestic oral hygiene.
2. Hormonal changes
Among the other causes that favor the onset of the problem related to swollen gums are hormonal changes. For this reason, pregnant or breastfeeding women and adolescents in the puberty phase suffer particularly from this disorder. Hormonal changes in fact influence both the retention of liquids and blood pressure, it is therefore more frequent that swelling of the gums occurs, even if temporarily, in these subjects.
3. Drug therapies
Some cases of swollen gums are instead directly related to the use of some drugs, for example an excessive use of anticoagulants. In particular, specific drug therapies can give rise to the pathology of gingival hyperplasia, that is, a consistent increase in the volume of the gums, much more complex than a simple swelling.
Medicines such as anti-epileptives, immunodepressors and calcium channel blockers can in fact cause inflammation of the gums, their thickening, sometimes even painful, and bleeding. The gingival tissue, in cases of hyperplasia, swells up to the point of also covering the surface of the tooth. Swollen gums to the point that they can become painful not only during the oral hygiene phases, but also during the simple chewing of foods.
3. Vitamin deficiency
Another cause of swollen gums, less common in western society, is the lack of vitamins, in particular vitamin C and vitamin K. The deficiency of these vitamins can lead to greater sensitivity at the gum level and is manifested precisely by the swelling of the gums and bleeding.
Whatever the cause that gave rise to the problem of swollen gums, it is important to intervene in time, because even the most trivial of the causes, such as insufficient oral hygiene could be, can lead to more serious consequences and also to more important economic expenses. the one supported for a simple deep cleaning session.