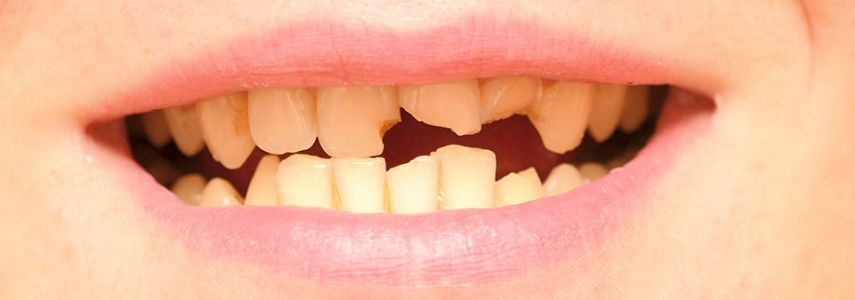
Tooth fracture is a very common problem but not all fractures are the same and can have different causes.
An experienced dentist won’t just tell you that a tooth is broken. A tooth can be defined as fractured when the fracture starts from the surface and continues towards the root of the tooth, a fracture of this type, which is not detected and treated in time, can cause the tooth to split in two parts.
Instead, it may happen that the fracture does not vertically cross the whole tooth up to the root but is limited to the upper part, frequent cases of fractures in fact affect parts most exposed to chewing, such as the cusps (the pointed parts of the tooth).
In other cases, the fractures are very small, therefore we are talking about cracking lines, this condition occurs when the micro-fractures affect only the surface part of the tooth, the enamel, and make the tooth particularly sensitive to thermal variations (hot / cold).
What situations can promote tooth fracture?
 Tooth fracture can derive from external trauma (accidents, falls …) or it can be caused by trauma during chewing (kernels, bones of the flesh …), more underestimated and perhaps less known are other causes caused by pre-existing dental pathologies.
Tooth fracture can derive from external trauma (accidents, falls …) or it can be caused by trauma during chewing (kernels, bones of the flesh …), more underestimated and perhaps less known are other causes caused by pre-existing dental pathologies.
The fracture of the tooth or of several teeth can in fact be a consequence of bruxism or the tendency to clench the teeth, the rubbing and the strong pressure between the dental arches, weakens and consumes the teeth to generate micro-fractures that if left untreated can cause damage worst.
The presence of periodontitis instead could facilitate the fracture of the tooth starting from the root.
In each of these cases, never underestimate the most common symptoms, namely pain during chewing and a permanent sensitivity to thermal variations; the control by an expert dentist will relieve you of any doubts and will clarify your ideas on which interventions are necessary.
The clinical choices on the therapy to be adopted may be different depending on the extent or depth of the fracture. A competent dentist will be able to assess the extent of the damage and expose you all possible solutions: from conservative therapy with filling or reconstruction of the affected part, to extraction where the fracture should affect a larger area of the tooth or also affect the root.
The possibilities of intervention are multiple because there are many clinical cases, there may be invisible microcracks in the human eye and not all dental centers have the instrumentation necessary to identify them.
Choosing a specialized dental center increases the guarantee of having correct diagnoses already at the first visit and of intervening in time on the problem before it can cause further damage to dental health.