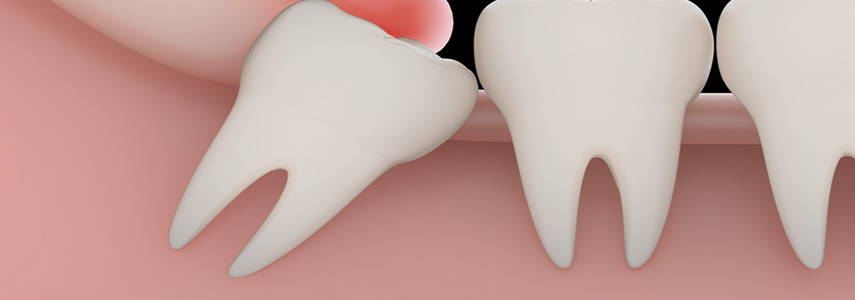
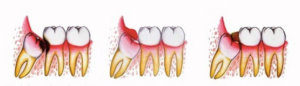
The wisdom tooth or third molar is one of the last elements to appear, usually the eruption of the eighth coincides with the age of majority, that’s why they are called wisdom teeth. The third molars are often, in spite of themselves, involved in numerous pathologies. The most common is that of the included tooth, wisdom teeth in fact do not always have the possibility of erupting in a natural way getting stuck in the gum. Their position also makes cleaning difficult, this condition creates more easily prerequisites for the onset of caries.
The set of clinical complications that can affect wisdom teeth has led in the past to the frequent choice of extracting third molars.
Is extraction the only way forward for wisdom teeth?
 Modern dentistry has assumed a more conservative position towards natural teeth, even in the case of wisdom teeth. When the wisdom teeth erupt normally and are correctly positioned inside the dental arches they contribute to the chewing function and the dentist should still tend to preserve them.
Modern dentistry has assumed a more conservative position towards natural teeth, even in the case of wisdom teeth. When the wisdom teeth erupt normally and are correctly positioned inside the dental arches they contribute to the chewing function and the dentist should still tend to preserve them.
An extraction operation of one or more wisdom teeth could represent a fairly complex clinical case.
The position of the third molars in fact implies a close contact with the lower alveolar nerve and with the maxillary sinus for the upper part, in addition to the possibility of having an abnormally placed root. A set of variables that must be considered in detail before choosing the possible extraction of the wisdom tooth.
In an excellent dental center you will never find a dentist who will undergo an extraction without carrying out an accurate clinical evaluation. Evaluation that can also make use of the most sophisticated diagnostic techniques, such as the Tac Cone Beam, which allows you to have a three-dimensional view of the position of the round of 16.
Because it is risky to proceed with the extraction of the wisdom tooth if it is not necessary
Each surgery has its contraindications. In particular, wisdom tooth extraction can lead to the following complications:
- injury to nerve structures;
- mandibular injury;
- paresthesia;
- edema in the affected area.
It is therefore reasonable to carefully evaluate an intervention for the extraction of one or more wisdom teeth. An experienced dentist will never proceed with the surgery unless it is strictly necessary.
Cases in which wisdom tooth extraction is indispensable
Wisdom tooth cannot be preserved in the following cases:
- it is an included tooth, that is, trapped in the gum;
- erupts off-axis and damages neighboring teeth;
- there is not enough space to guarantee its eruption;
- an acute infection is in progress.
Always be wary of diagnoses that involve too easy extractions, each intervention must be planned and justified by careful clinical investigations.